The LARGE function in Excel is a fundamental tool in the realm of statistical analysis, designed to pinpoint the largest value within a given array or cell range. This article serves as an extensive guide on harnessing the power of the LARGE function in Excel. We will walk you through detailed steps on how to effectively use this function, including practical examples to illustrate its application.
Supported versions
- All Excel versions
Excel LARGE Function's Syntax
The syntax of the Excel LARGE function is straightforward and precise, allowing users to easily retrieve the k-th largest value from a specified array of numbers. Presented in a simple format:
- array: This is the set of numbers from which you intend to find the k-th largest value. The array can be a range of cells or a collection of numerical values.
- k: This is an integer that determines the specific position from the largest value that you wish to obtain. For example, if k is set to 1, the function will return the largest value; if k is set to 2, it will return the second largest value, and so on.
Example Usages of Excel LARGE Function
1. Finding the Largest k-th number with the LARGE Function
In this example, we illustrate the application of the Excel LARGE function to find the k-th largest number in a dataset.
This formula is used to determine the 5th largest number within a given range. Let's consider a range named "Speed". When this formula is applied, it identifies and returns the 5th largest value from this range. For instance, if the top values in the "Speed" range are {120; 100; 100; 90; 90; ...}, the formula yields 90.
Note that the LARGE function accounts for each occurrence of a value within the range. In our example, although 90 appears as the 3rd largest number, the function recognizes both instances of 100, treating each occurrence separately. This nuance ensures that the 'k' in the formula accurately represents the k-th position in the sorted list of values, regardless of any repetitions. This aspect of the LARGE function in Excel makes it a reliable tool for precise statistical analysis and data management tasks.
2. Finding the Largest k-th date/time with the LARGE Function
The Excel LARGE function is versatile, extending its utility beyond just numerical values to also encompass date and time data, which Excel internally treats as numbers. This functionality allows for the identification of the k-th latest date or time in a given set.
In this example, the formula utilizes the LARGE function to find the 5th latest date or time value from the 'ReleaseDate' range. By inputting '5' as the 'k' value, the formula will search through the range and return the 5th latest date/time. This capability is particularly useful in scenarios where sorting through chronological data is necessary, such as analyzing product release dates, scheduling events, or managing timelines.
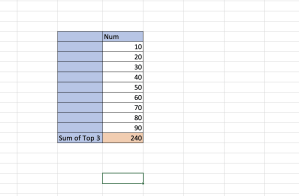
3. Finding the Sum of the Top 3 Values's with the LARGE and SUMPRODUCT Functions
The SUMPRODUCT function in Excel, belonging to the Math & Trig category, is a multifaceted tool that goes beyond merely multiplying and summing arrays. It stands out for its unique capability to handle and manipulate arrays, making it an invaluable asset in advanced Excel data analysis. SUMPRODUCT can perform various complex operations, such as comparing arrays, summing or counting based on multiple criteria, calculating weighted averages, and more.
Incorporating the SUMPRODUCT function into our earlier discussion, particularly when combined with the LARGE function, unveils its potential in sophisticated data manipulation techniques. This combination is adept at aggregating significant values, as exemplified in the formula:
Here, the LARGE function is employed to extract the top three values from the range I8:I16, as indicated by the array `{1,2,3}`. Following this, SUMPRODUCT steps in to perform its core function – it multiplies these identified values (in this case, it's effectively the same as summing them since they are singular values from the LARGE function) and returns their cumulative sum.
Summary and Tips
- Core Usage: Employ the LARGE function in Excel when you need to determine the k-th largest value from a set of data. This function is especially useful in data analysis, statistical research, or any scenario where ranking values is important.
- Flexibility with Data Types: The LARGE function is not limited to just numerical values; it also adeptly handles date and time values treated as numbers in Excel. This feature expands its utility across various data types, making it an essential tool for a broad range of applications.
- Simple Yet Effective: For instance, `=LARGE(array, 1)` is a straightforward formula that fetches the largest value in a given array or range. Interestingly, this functionality mirrors that of the MAX function in Excel.
- Complementary Functions: To complement the capabilities of the LARGE function, consider exploring the SMALL function in Excel. The SMALL function is designed to find the k-th smallest value in an array, providing a useful contrast to the LARGE function for comprehensive data analysis.
- See the SMALL function to find the k-th smallest value from an array.
Issues
When working with the Excel LARGE function, it's important to be aware of certain scenarios that can lead to errors. One of the most common issues arises when the function encounters specific types of input irregularities:
1. Empty Array Issue: If the 'array' parameter in the `LARGE(array, k)` function is set to an empty range or array, Excel cannot find any value to return. This lack of data results in a `#NUM!` error, indicating that the function cannot perform its calculation due to the absence of numerical values.
2. Invalid 'k' Value: Similarly, the function will return a `#NUM!` error if the 'k' parameter does not correspond to a valid position within the array or range. This situation occurs if 'k' is set to a number larger than the number of elements in the array, or if it's a non-numeric value. For instance, if 'k' is 5, but there are only 3 numbers in the array, Excel cannot provide the 5th largest value and thus generates an error.
Being aware of these potential issues is crucial for effectively using the LARGE function in Excel. Proper data preparation and validation of the 'k' value can help avoid these errors and ensure the function performs as expected, providing accurate and useful results in your data analysis tasks.




 .
.