In many organizations, Excel remains the primary tool for data analysis, reporting, and decision-making. As business needs evolve, more advanced or specialized models are developed—often requiring secure and scalable methods to share them across teams. This is where SpreadsheetWeb can make a difference. By deploying complex spreadsheet models as a web-based service, SpreadsheetWeb allows you to expose select inputs and outputs via an API.
An incredibly handy feature is that you can continue to work directly in Excel to access these models—thanks to Power Query. Power Query lets you pull data from various sources, including APIs, and transform it within Excel. This approach is beneficial if you want to keep the details of your complex or sensitive spreadsheet models confidential while still enabling others to manipulate the model’s inputs and capture outputs in real time.
In this guide, we’ll walk through how to connect to the SpreadsheetWeb API directly from Excel’s Power Query, making it easier than ever to integrate your web-based models with your familiar Excel environment.
Understanding the SpreadsheetWeb API
Before getting started with Power Query, it’s important to understand how the SpreadsheetWeb API works. The API typically revolves around:
- Endpoints: These URLs define where you can send or request data. SpreadsheetWeb offers different endpoints for calculation, authentication (if required), and other functions.
- Authentication: Depending on your security and usage requirements, you can connect to your SpreadsheetWeb application with or without authentication:
- Unauthenticated Access: Ideal for simple cases or demonstrations where security is not a primary concern.
- Authenticated Access: Necessary for production systems or sensitive data. A token must be obtained from a dedicated endpoint and then used in subsequent requests to retrieve your model’s results.
Choosing between unauthenticated and authenticated access depends on your security policies, the nature of your data, and how you intend to share your model within the organization.
Preparing Excel for Power Query
Matching Cells to the SpreadsheetWeb Model
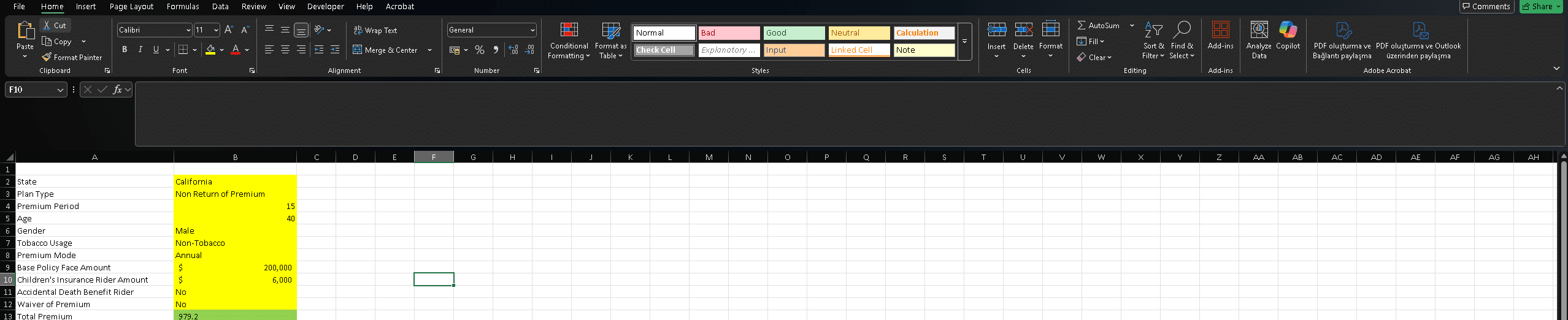
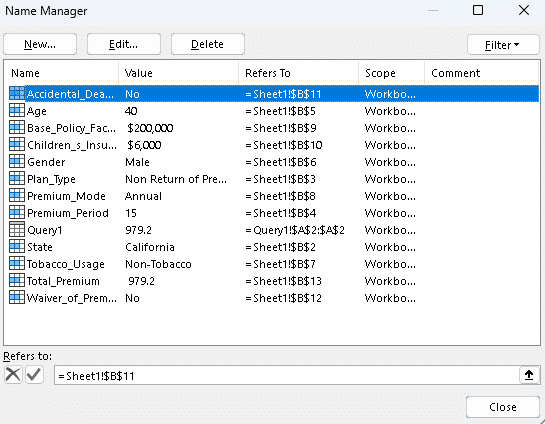
In this example, we’ll use a life insurance pricing model to calculate premium rates. The model includes several input fields, highlighted in yellow, and a single output—the calculated premium—highlighted in green, as shown in the screenshot below. While the rest of the Excel workbook contains supporting lookup tables and background calculations, these are not relevant for the API integration. Each input and output cell is assigned a named range to simplify the construction of API requests.
To ensure seamless integration, it’s important that your local Excel file contains matching cells for the inputs and outputs defined in the SpreadsheetWeb model. This alignment allows you to easily populate input values and retrieve output data from the API. The screenshot below shows the Excel file used to connect to the SpreadsheetWeb API. As you can see, it includes matching input and output cells—but no embedded logic—since all calculations will be executed remotely via SpreadsheetWeb.
Checking Excel Power Query Compatibility
Modern versions of Excel (Excel 2016 and later) have Power Query built-in under the “Get Data” menu. If you’re on an older version of Excel (such as 2010 or 2013), you may need to install the Power Query add-in.
- Open Excel.
- Go to File > Options > Add-ins.
- Ensure that Microsoft Power Query (or “Get & Transform” in some versions) is enabled.
Configuring Privacy and Security Settings
Since you’ll be connecting to an external API, ensure your Excel settings allow data connections from external sources. Go to File > Options > Trust Center > Trust Center Settings. Under External Content, verify that data connections are allowed.
Establishing a Connection to SpreadsheetWeb
Once Excel is ready, you can begin setting up the data connection via Power Query. This process differs slightly depending on whether you’re using unauthenticated or authenticated access.
🔒 Unauthenticated Access
When to Use It
- For demonstration or testing purposes where security is not a major concern.
- When your SpreadsheetWeb application is publicly available or does not require credentials.
Information Needed
- Endpoint: Typically the URL pointing to your model or calculation API.
- Workspace ID and Application ID: Identifiers for your particular SpreadsheetWeb application.
Sample M Query Code (Unauthenticated):
let
State = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="State"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
PlanType = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Plan_Type"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
PremiumPeriod = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Premium_Period"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
Age = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Age"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
Gender = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Gender"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
TobaccoUsage = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Tobacco_Usage"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
PremiumMode = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Premium_Mode"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
BasePolicyFaceAmount = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Base_Policy_Face_Amount"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
ChildrenInsuranceRiderAmount = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Children_s_Insurance_Rider_Amount"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
AccidentalDeathBenefitRider = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Accidental_Death_Benefit_Rider"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
WaiverOfPremium = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Waiver_of_Premium"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
ApiUrl = "https://api.spreadsheetweb.com/calculations/calculatesinglesimple",
AccessToken = "<TOKEN>",
RequestBody = Json.FromValue([
request = [
workspaceId = "WORKSPACE_ID",
applicationId = "APPLICATION_ID",
inputs = [
AccidentalDeath = AccidentalDeathBenefitRider,
ChildrenRiderAmount = ChildrenInsuranceRiderAmount,
Class = TobaccoUsage,
CustomerName = null,
FaceAmount = BasePolicyFaceAmount,
Gender = Gender,
IssueAge = Age,
PlanType = PlanType,
PremiumMode = PremiumMode,
PremiumPeriod = PremiumPeriod,
State = State,
WaiverPremium = WaiverOfPremium
],
outputs = {"TotalPremium"}
]
]),
Headers = [
#"Content-Type" = "application/json",
#"Authorization" = "Bearer " & AccessToken
],
ApiResponse = Web.Contents(ApiUrl, [
Headers = Headers,
Content = RequestBody
]),
JsonResponse = Json.Document(ApiResponse),
Response = JsonResponse[response],
TotalPremium = Response[outputs][TotalPremium],
#"Converted to Table" = #table(1, {{TotalPremium}})
in
#"Converted to Table"
Explanation: This code extracts data from named ranges in Excel, builds a JSON request body, and sends it to the SpreadsheetWeb API. It then parses the JSON response to extract the calculated premium.
🔐 Authenticated Access
When to Use It
- If your SpreadsheetWeb application requires secure login.
- When sensitive data is involved, and you need to ensure only authorized personnel have access.
Additional Information Needed
- API Key and Secret (or credentials) to generate a token.
- Two API calls: One for authentication/token retrieval and another for the calculation itself using the obtained token.
Sample M Query Code (Authenticated):
let
TokenUrl = "https://identity.spreadsheetweb.com/connect/token",
TokenBody = "grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET",
TokenResponse = Web.Contents(TokenUrl, [
Headers = [#"Content-Type" = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"],
Content = Text.ToBinary(TokenBody)
]),
TokenJson = Json.Document(TokenResponse),
AccessToken = TokenJson[access_token],
State = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="State"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
PlanType = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Plan_Type"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
PremiumPeriod = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Premium_Period"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
Age = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Age"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
Gender = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Gender"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
TobaccoUsage = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Tobacco_Usage"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
PremiumMode = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Premium_Mode"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
BasePolicyFaceAmount = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Base_Policy_Face_Amount"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
ChildrenInsuranceRiderAmount = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Children_s_Insurance_Rider_Amount"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
AccidentalDeathBenefitRider = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Accidental_Death_Benefit_Rider"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
WaiverOfPremium = Excel.CurrentWorkbook(){[Name="Waiver_of_Premium"]}[Content]{0}[Column1],
ApiUrl = "https://api.spreadsheetweb.com/calculations/calculatesingle",
RequestBody = Json.FromValue([
request = [
workspaceId = "WORKSPACE_ID",
applicationId = "APPLICATION_ID",
transactionSequenceId = 2,
request = [
input = [
calculation = [
inputs = {
[ reference = "AccidentalDeath", value = {{ [ value = AccidentalDeathBenefitRider ] }} ],
[ reference = "ChildrenRiderAmount", value = {{ [ value = ChildrenInsuranceRiderAmount ] }} ],
[ reference = "Class", value = {{ [ value = TobaccoUsage ] }} ],
[ reference = "CustomerName", value = {{ [ value = null ] }} ],
[ reference = "FaceAmount", value = {{ [ value = BasePolicyFaceAmount ] }} ],
[ reference = "Gender", value = {{ [ value = Gender ] }} ],
[ reference = "IssueAge", value = {{ [ value = Age ] }} ],
[ reference = "PlanType", value = {{ [ value = PlanType ] }} ],
[ reference = "PremiumMode", value = {{ [ value = PremiumMode ] }} ],
[ reference = "PremiumPeriod", value = {{ [ value = PremiumPeriod ] }} ],
[ reference = "State", value = {{ [ value = State ] }} ],
[ reference = "WaiverPremium", value = {{ [ value = WaiverOfPremium ] }} ]
},
outputs = { "TotalPremium" }
]
]
],
transactionDate = null
]
]),
ApiResponse = Web.Contents(ApiUrl, [
Headers = [
#"Content-Type" = "application/json",
#"Authorization" = "Bearer " & AccessToken
],
Content = RequestBody
]),
JsonResponse = Json.Document(ApiResponse),
OuterResponse = JsonResponse[response],
InnerResponse = OuterResponse[response],
Calculation = InnerResponse[output][calculation],
OutputsList = Calculation[outputs],
FirstOutput = OutputsList{0},
PremiumValue = FirstOutput[value]{0}{0}[value]
in
PremiumValue
Explanation: This script first retrieves a token using client credentials, then performs a secure API call to the SpreadsheetWeb calculation endpoint and parses the output value.
Testing Excel Power Query
After setting up your queries:
- Refresh the Power Query data to ensure Excel can pull data from the SpreadsheetWeb API successfully.
- Check if the returned values (outputs) match the numbers from the Excel model.
- Adjust input parameters and re-check to confirm that real-time calculations are happening.
- For authenticated connections, confirm that the token is being generated properly. If you receive errors (like a 401 Unauthorized), double-check your credentials and token-handling steps.
Conclusion
With Power Query, you can tap directly into your SpreadsheetWeb models right from Excel, keeping your workflow centralized and accessible. Whether you opt for unauthenticated connections for simple demos or authenticated connections for secure enterprise use, Power Query provides a versatile toolset to integrate complex or sensitive models without exposing the underlying spreadsheet logic.
By following the steps outlined above, you can:
- Maintain data security by granting access only to specific inputs and outputs.
- Leverage Excel’s familiar interface to drive real-time calculations via the SpreadsheetWeb API.
- Scale your spreadsheet models beyond traditional limitations, offering a more robust solution for cross-departmental collaboration.
If you have any questions or need more detailed guidance, don’t hesitate to reach out or explore the official SpreadsheetWeb documentation for further information. Happy querying!