The Excel COLUMN function is a powerful formula within the software's suite of Lookup & Reference formulas. Its primary function is to retrieve the column number of a specific reference. In this comprehensive guide, we will go into the details of the Excel COLUMN function, providing you with a thorough understanding of its functionality and applications.
Throughout this guide, we will not only demonstrate how to use the Excel COLUMN function but also share invaluable tips and techniques to enhance your understanding. Additionally, we will explore error handling methods to ensure you can confidently work with this function, even when dealing with unexpected issues or data anomalies.
Supported Versions
- All Excel versions
Syntax of the COLUMN Function
The COLUMN function returns the column number of a specific reference.
- `([reference])`: Inside the parentheses, you typically provide an argument or input to the function. It should be a reference to a cell or a range of cells for which you want to determine the column number.
So, in plain language, the `
For example, if you were to use this function in a real Excel formula, it might look like this:
`=COLUMN(A1)`
In this example, `A1` is the reference, and the function would return the column number of cell A1, which is 1 since it is in the first column.
| [reference] | Optional. A valid reference. |
Examples of COLUMN Function
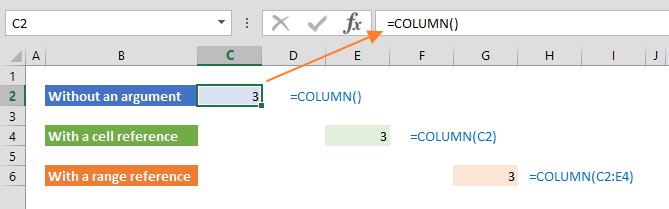
Example 1: COLUMN Function with No Arguments
When no specific arguments are provided, the COLUMN function serves the purpose of identifying and returning the column number corresponding to the location where the formula is placed within the spreadsheet. This means that by simply inputting '=COLUMN()' in a cell, the function will automatically determine the column number of that particular cell, offering a convenient way to dynamically adapt calculations or formatting based on the column's position in the spreadsheet layout.
Example 2: COLUMN Formula with A Cell Reference
If you provide a valid cell reference as an argument, the `COLUMN` function will return the column number corresponding to that reference. In other words, if you input a cell reference, the function will output the specific column number associated with that reference in the spreadsheet.
Example 3: COLUMN Function with A Range Reference
When you provide a range reference as an argument to the `COLUMN` function, it returns the column number of the leftmost column within that range. However, with the introduction of dynamic arrays, the `COLUMN` function can become more versatile. In such cases, when you use a range reference as an argument, it can return not just the column number of the leftmost column but also an array of column numbers representing all the columns within that range reference. This enhanced functionality allows you to obtain a list of column numbers, which can be particularly useful for various data analysis and manipulation tasks in spreadsheets.
Example 4: Generating Number Series using COLUMN Formula
One frequently employed method for leveraging the Excel COLUMN function involves determining the column number associated with a specific cell reference. By applying the COLUMN function across multiple adjacent columns, you can effortlessly generate a sequence of numbers.
In our illustrative example, we positioned the COLUMN function within a cell located in column 3, which corresponds to column C. Subsequently, we subtracted 2 from the column number yielded by the function. As a result, this computation provided us with the value 1, signifying that the cell was in the third column.
Now, when we replicate the same formula across various cells in column I, it unfolds into a series of numbers spanning from 1 through 7. This sequential progression is particularly valuable for a wide range of spreadsheet tasks, as it enables the automatic generation of numerical sequences, simplifying data manipulation and analysis.
Error Handling in COLUMN Function
The COLUMN function in Excel is quite straightforward, but there are a few scenarios where you might encounter errors or unexpected behavior:
#REF! Error: If you provide a reference to a cell or range that doesn't exist, the COLUMN function will return a #REF! error. This can happen if you delete a column that's referenced in your COLUMN function. To prevent this, ensure that the cell or range you reference is valid and exists in your worksheet.
If you're using the COLUMN function in a larger formula and want to handle possible errors, you can use the IFERROR function. This allows you to specify an alternative action if an error is encountered. For example: =IFERROR(COLUMN(A1), "Error") would return "Error" if the COLUMN function fails.
Tips for COLUMN Formula in Excel
When working with Excel or other spreadsheet software, it's essential to have a good understanding of various functions that can help you manipulate and analyze your data effectively. Two such functions are the COLUMNS function and the ROW function.
- COLUMNS Function: One practical function is COLUMNS, which becomes handy when you need to count the number of columns within a specified reference. Whether you're dealing with a single range of cells or an array, the COLUMNS function provides a quick and accurate way to determine how many columns are included. This function can be particularly valuable when setting up dynamic formulas or defining the dimensions of a dataset.
- ROW Function: Conversely, the ROW function serves the purpose of extracting the row number of a given reference. It's a versatile tool that allows you to pinpoint the exact row where a specific piece of data is located. By incorporating the ROW function into your formulas, you can easily retrieve and work with data from different rows within your spreadsheet.
By incorporating both the COLUMNS and ROW functions into your spreadsheet work, you empower yourself to navigate and manipulate data efficiently. Whether you're building complex formulas or simply organizing your data, these functions are invaluable tools in the world of spreadsheet analysis.