The Excel SORTBY function is an effective tool for organizing data in spreadsheets. It simplifies the process of arranging values within a specific range or array, using related data from another range or array to determine the order. One significant aspect of the SORTBY function is its compatibility with Excel's Dynamic Array feature. Dynamic Arrays allow for the automatic filling of a range of cells with values derived from a single formula, a process known as 'spilling'. This innovative feature moves beyond the traditional constraints of array formulas, offering a more adaptable and efficient way to handle data. When used in conjunction with Dynamic Arrays, the SORTBY function facilitates more versatile sorting options in Excel, including sorting by various criteria such as length, character, and other custom-defined parameters.
Supported Versions
The `SORTBY` function in Microsoft Excel is available starting from Excel 365 and Excel 2019. It's part of the dynamic array functions introduced in these versions. If you're using an older version of Excel, such as Excel 2016 or earlier, this function won't be available. Excel 365, being a part of the Office 365 subscription service, continuously receives new feature updates, including functions like `SORTBY`. Excel 2019, while not subscription-based, also includes this function but doesn't receive the same continuous feature updates as Excel 365.
Syntax of the Excel SORTBY Function
Function Parameters
- Array: This is the primary range or array that you want to sort. It can include multiple columns or rows, and the SORTBY function will reorder the entire array based on the sorting criteria you provide.
- By\_array1: This refers to the first array or range that will dictate the sorting order of the primary array. The SORTBY function uses the values in this array to determine the sequence of the sorted data.
- Sort\_order1: An optional parameter. This numeric value specifies the sorting order for 'by\_array1'. The default setting is 1, which corresponds to an ascending sort. If you prefer a descending order, you can set this parameter to -1.
- By\_arrayN: This represents the nth array or range you want to use for sorting. Excel SORTBY function allows multiple sorting criteria, providing flexibility for complex data organization tasks, such as sorting by multiple columns or using a custom sort order.
- Sort\_orderN: Also optional, this numeric value sets the sorting order for 'by\_arrayN'. Like with the first sorting order, the default is 1 for ascending sorting. To sort in descending order, use -1.
Example Usages of the Excel SORTBY Function
Example 1:
Let's consider an example using the Excel SORTBY function. Imagine you have a sales report with two key columns: 'Product Type' and 'Sales Amount'. You want to sort the report first by 'Product Type' in alphabetical order and then by 'Sales Amount' in descending order, to see the highest selling products within each category.
Suppose your data table has the following columns - 'Product Type' (Column A) and 'Sales Amount' (Column B).
- Data Setup: Your table lists various product types such as 'Electronics', 'Clothing', 'Furniture', etc., along with their corresponding sales amounts.
- SORTBY Function: Use the formula:
- ==SORTBY(A2:B10,B2:B10,-1)
- This formula sorts your data first by 'Product Type' in descending order (1 for ascending), and then within each product type, it sorts the products by 'Sales Amount' in descending order (-1 for descending).
- Result: Once you apply this formula, your table will reorganize. All products will be grouped under their respective product types in alphabetical order. Within each product type category, the products will be listed from the highest to the lowest sales amount.
For instance, under 'Clothing', you would first see the most sold clothing item, followed by the next highest, and so on, before moving onto the 'Electronics' category where the same pattern follows.
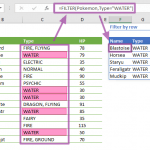
Example 2:
This example demonstrates an application of the Excel SORTBY function. In this case, the formula =SORTBY(NameAndType, HP, -1) effectively organizes the data from the named range 'NameAndType'. It achieves this by sorting according to the values in the named range 'HP'. The key aspect here is the use of -1 as the third argument in the formula, which directs the SORTBY function to sort the data in descending order. This means the highest values in 'HP' will appear first in the sorted list, providing a clear and efficient way to analyze data where the order of values is a critical factor.
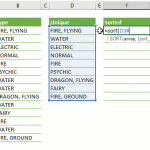
Example 3: Sort by multiple columns
This formula exemplifies the use of the Excel SORTBY function for sorting multiple columns in a complex manner. Here, the 'Pokemon' column is being sorted based on two criteria: 'Type' and 'Name'. The unique aspect of this formula is the application of different sorting orders for each criterion.
- Sorting by 'Type' in Descending Order: The part of the formula `, Type, -1` specifies that the 'Type' column should be sorted in descending order. This means that the values in the 'Type' column are arranged from the highest to the lowest, playing a primary role in the sorting sequence.
- Sorting by 'Name' in Ascending Order: The segment `, Name, 1` of the formula indicates that the 'Name' column should be sorted in ascending order. This sorting is applied after the 'Type' sorting, arranging the names in alphabetical order (from A to Z) within each type category.
By using SORTBY in this way, the data in the 'Pokemon' column is organized first by the 'Type' in a descending sequence and then by 'Name' in an ascending order within each type category.
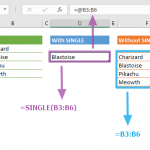
Example 4: Shuffle Values
This example demonstrates a creative application of the Excel SORTBY function to shuffle values in a list. Although SORTBY is typically used for systematic sorting, it can be adapted to randomize the order of a list when combined with the RANDARRAY function. Here's how it works:
The formula `=SORTBY(Name, RANDARRAY(COUNTA(Name)))` uses the RANDARRAY function to create an array of random numbers. These numbers serve as the sorting criteria for the SORTBY function. Since the numbers are randomly generated, the SORTBY function effectively shuffles the values in the 'Name' array.
A key component of this formula is the COUNTA function, which dynamically calculates the number of non-empty cells in the 'Name' range. This ensures that the RANDARRAY function generates the correct number of random values to match the size of the 'Name' array.
It's important to note that with each recalculation in Excel, the RANDARRAY function generates a new set of random numbers. Consequently, the order of the values in the 'Name' array will change every time the worksheet recalculates, providing a new, randomized order each time. This technique can be particularly useful in scenarios where you need to randomize the order of items, like in a draw or a lottery system, within Excel.
Excel SORTBY Function Tips
Choosing Between SORTBY and SORT: When your sorting task involves organizing a range or array based on the values in a different range or array, the SORTBY function is your go-to choice. This is because SORTBY references ranges directly, making it adept at handling changes in columns without relying on index numbers. This feature of the SORTBY function makes it particularly useful for dynamic sorting in Excel, such as when dealing with multiple columns, custom sorting, or sorting by formulas.
Utilizing SORT for Self-Referential Lists: On the other hand, if you're looking to sort a list based on its own values, the SORT function is more appropriate. This function is straightforward and efficient for simple sorting tasks where the sorting criteria are within the same array or range being sorted. For example, if you're sorting a single column in ascending or descending order based purely on the values within that column, the SORT function is a straightforward and effective solution.
Both these functions, SORTBY and SORT, offer flexibility and efficiency for different sorting scenarios in Excel. Whether you're looking to perform a custom sort in Excel, sort by multiple criteria, or need a simple ascending or descending order sort, choosing the right function is crucial for optimal data management.
Issues and Error Handling on Excel SORTBY Function
Understanding and Resolving the #SPILL! Error in Excel
The #SPILL! error in Excel typically occurs when there is insufficient space to display the results of a formula that uses dynamic array functions, such as the SORTBY function. This issue arises when the cells that the function needs to "spill" into are occupied by other data or formulas. Here's how to address this error:
- Identify the Obstructed Cells: Excel visually indicates the range where the spill should occur with dashed lines. This helps you quickly identify which cells are causing the issue.
- Clear the Blocked Range: To resolve the #SPILL! error, you need to clear or move the contents that are blocking the spill range. Ensure that the area below or adjacent to your formula (depending on the direction of the spill) is empty.
- Automatic Update: Once the obstructing contents are removed, Excel will automatically recalculate the formula and display the results correctly, provided there's now enough space for the spill.
The #VALUE! Error in Excel's SORTBY Function
The #VALUE! error in Excel's SORTBY function can occur under two primary scenarios:
- Mismatched Array Sizes: This error appears when the 'array' and 'by_array' arguments in the SORTBY function do not match in size. For the function to work correctly, both these arrays must be of equal length. This means the range or array you want to sort (array) and the range or array you are using as the basis for sorting (by_array) need to have the same number of rows or columns. If there's a discrepancy in size, Excel cannot perform the sort and consequently returns the #VALUE! error.
- Incorrect [sort_order] Values: The #VALUE! error also pops up if the [sort_order] argument is set to any value other than 1 or -1. In the SORTBY function, [sort_order] specifies the direction of the sort: 1 for ascending order and -1 for descending order. Any other numeric or non-numeric value assigned to this argument is invalid and leads Excel to generate the #VALUE! error.
To prevent or resolve the #VALUE! error, ensure that your 'array' and 'by_array' are aligned in terms of size and that the [sort_order] is correctly set to either 1 or -1. This attention to detail is crucial for the smooth functioning of the SORTBY function and accurate data sorting in Excel.