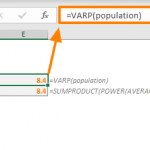
The VARPA function in Excel is a powerful statistical function designed to calculate and return the variance of a population by evaluating text and logical values. As one of the essential Excel functions for statistical analysis, This Excel function provides a general insight into the dispersion of data points within a dataset. This variance measurement is crucial for various applications, such as assessing risk in investments or determining standard deviation. In this guide, we will delve into the practical application of the VARPA Excel function, offering insights into its usage, along with valuable tips and error handling methods to enhance your proficiency with Excel functions.
Supported versions
- Excel 2003 and newer versions
VARPA Function Syntax
Arguments
| number1 | The first number argument corresponding to the entire population. |
| [number2] | Optional. Other arguments corresponding to the entire population. Up to 254 can be added. |
VARPA Function Example
The function accepts numeric values as its arguments. Any type of text or logical values will be ignored. You can use range references or static values just like in any other formula.
The function calculates the variance using the following function:
- x: population mean (average)
- x ̅: element of the population
- n: population size
Here is the comparison of the two approaches:
SUMPRODUCT(POWER(AVERAGE(evaluated)-evaluated,2))/
COUNT(evaluated))
The formulas are using the named range population (B5:B10).
Tips
- The VARPA function assumes that its arguments represent the entire population. If your data is a sample of the population, use VARA.
- The VARPA function evaluates text and logical values like TRUE and FALSE. If you want to ignore non-numeric values, use the VAR.P function instead.
- Empty cells are ignored.
Issues
- Any error in the arguments will cause the function to return an error.
This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of how to leverage the VARPA Excel function, from its fundamental application to advanced tips and error handling techniques. As you continue to explore and incorporate Excel functions into your data analysis endeavors, mastering the VARPA function contributes to a robust skill set for handling statistical computations within the Excel environment. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, the VARPA function stands as a versatile asset, enhancing the accuracy and depth of your statistical analyses in Excel.