To effectively prevent duplicates in Excel, the Data Validation feature paired with the COUNTIF function serves as a robust solution. This guide illustrates how to harness these tools to ensure data integrity by eliminating the chance of duplicate entries.
Step-by-Step Guide to Preventing Duplicates in Excel
1. Identify Your Data Range: First, decide on the range within your Excel sheet that requires duplicate prevention. This could be any column or row where unique entries are crucial.
2. Access Data Validation: Navigate to the 'Data' tab on Excel's ribbon and locate the 'Data Validation' icon. This feature is key to setting up rules that govern what data can be entered into your cells.
3. Set Up Custom Validation: Within the Data Validation dialog, select 'Custom' from the 'Allow' dropdown menu. This option enables you to define a specific rule using a formula.
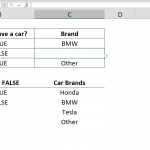
4. Implement COUNTIF Formula: In the formula field, input the validation rule using the COUNTIF function. The syntax should look like this: =COUNTIF($C$5:$C$10, C5) < 2. This formula checks for the uniqueness of the entry in the specified range ($C$5:$C$10), ensuring that any given value doesn't appear more than once.
5. Finalize Your Rule: After entering the formula, click 'OK' to apply the data validation rule. Excel will now prevent the entry of duplicate values within the specified range, aligning with your unique data requirements.
Understanding the COUNTIF Function
The COUNTIF function is instrumental in identifying duplicates. It counts the number of times a specific value appears in a range. By setting the condition < 2, we ensure that a value can only appear once, effectively preventing duplicates.
When applied to prevent duplicates in Excel, the COUNTIF function is set up to count how many times the value in the currently evaluated cell appears within a specified range. If the count exceeds 1, it indicates the presence of a duplicate.
In a validation rule like =COUNTIF($C$5:$C$10, C5) < 2, COUNTIF checks the range $C$5:$C$10 to see how many times the value in cell C5 appears. If the value in C5 appears more than once in this range, the count would be 2 or more, and the condition < 2 would be false, triggering Excel's data validation to prevent the duplicate entry.
Excel Data Validation Feature to Prevent Duplicates
Excel Data Validation feature is a great tool to ensure that users enter the correct value. As well as its preset options to restrict user entries, the tool allows you to create your own lists by using formulas. Selecting Custom option in Allow dropdown shows the Formula input that you can enter your own validation formula.
The validation formulas works like Conditional Formatting formulas. When a data validation rule is set, Excel allows user to enter a value if the formula returns TRUE values. You can find formula samples about Conditional Formatting in the following articles: How to highlight … examples
Absolute vs. Relative References
In the COUNTIF formula used for validation, the range is an absolute reference (e.g., $C$5:$C$10), ensuring it remains constant. The cell being validated (e.g., C5) is a relative reference, allowing Excel to adjust the cell reference dynamically as the formula is applied to different cells in the range.
If you select the 5th cell in the list (C9) and check the Data Validation formula, you can see formula is altered as below
=COUNTIF($C$5:$C$10,C9)<2.
Practical Applications of Preventing Duplicates
By integrating the COUNTIF function with Excel's Data Validation feature, users gain a powerful mechanism to maintain data accuracy and consistency. This approach is especially beneficial in scenarios where data uniqueness is required. Here are a few practical applications of preventing duplicates:
Financial and Accounting: Preventing duplicates in financial models and accounting spreadsheets can help in managing transaction records, where each entry must be unique to avoid double-counting or inflating financial figures. For instance, invoice or receipt numbers in a ledger must be unique to accurately track payments and expenditures, preventing financial discrepancies.
Inventory Management: In inventory management systems, duplicate entries can lead to incorrect stock levels, resulting in overstocking or stockouts. By implementing data validation to prevent duplicates, businesses can maintain accurate inventory records, ensuring each item's unique identifier (like SKU numbers) is entered only once. This accuracy is crucial for inventory forecasting, ordering, and stock level optimization.
Human Resources: In HR and recruitment processes, duplicate entries in applicant tracking systems or employee databases can complicate HR operations. Preventing duplicates helps in maintaining a clean database of candidates and employees, facilitating efficient recruitment processes, employee management, and compliance with regulatory requirements.