The AVERAGE Function
The AVERAGE function is a vital tool in spreadsheet applications like Excel or Google Sheets, simplifying the calculation of the arithmetic mean for a range of cells. This function is invaluable for tasks like data analysis and financial modeling.
To use the AVERAGE function, select a range of cells with numeric data, and it automatically computes their average, saving time and minimizing errors. Whether dealing with financial data or scientific figures, the AVERAGE function streamlines the process.
To apply the function, input "=AVERAGE(A1:A10)" for a range like A1 to A10 representing monthly sales. This guide goes beyond the basics, offering tips for enhanced proficiency and error handling. Understanding these nuances ensures accurate results and empowers you to navigate complex datasets confidently.
In summary, the AVERAGE function is a powerful asset, and this guide provides not only basic usage but also tips and error-handling techniques for efficient data analysis in spreadsheet software. Mastering these aspects enhances your ability to make informed decisions in personal or professional settings.
Supported versions
- AVERAGE in Excel is supported in all versions.
Syntax
AVERAGE Function Arguments
| number1 | The first number or numbers you want to calculate. You can put a static number like 4, a cell reference like B6, or a cell range like B2:B8. |
| [number2] | Optional. The second number or numbers you want to calculate up to 255 numbers. |
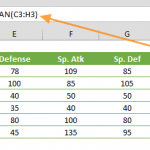
Examples of The AVERAGE in Excel
Tips
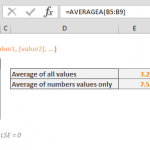
Note that the function disregards string values. It's important to note that date or time values are treated as serial numbers in Excel, not as strings. If you intend to compute the average of values based on specific criteria, consider utilizing the AVERAGEIF function or the AVERAGEIFS function.
Issues
#####
The column is too narrow for the result of the function. The solution is to increase the width of the column.
Error
If there is an error in referred cells or ranges,it returns the same error.